By PATRICK CAIRNS
It seems logical to believe that the performance of a country’s stock market is linked to the state of its economy. After all, if GDP growth is strong, company profits are good, and that should help share prices.
Economic prospects are even often used to identify which stock markets are likely to perform in future. If a country is experiencing positive GDP growth, then investors are encouraged to see it as a good place to put their money.
What the evidence reveals
Yet several studies have shown that this link is actually weak. A comprehensive analysis of 21 countries over more than 100 years by the authors of the book Triumph of the Optimists found mixed results between GDP growth and stock market performance.
An MSCI analysis in 2010 found similar results. Most notably, for the 60 year period from 1958 to 2008, Spain and Belgium enjoyed real growth in their economies of between 3% and 4% per year, yet the real returns from their stock markets over this same time were negative.
One of the clearest examples of the potential breakdown between a country’s economic performance and that of its stock market has been Japan. Since 1989 the country has grown its economy at over 1.5% per year, yet the Nikkei 225 Index is still well below its December 1989 peak. That is a period of more than 30 years in which Japan’s GDP growth has not been reflected in broad market returns.
A closer look
This doesn’t only occur over the long term either. It can also be play out from year to year.
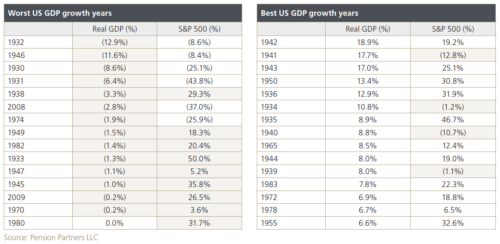
The tables below, which consider the last 90 years of GDP growth in the US, make this clear. On the left are the 15 calendar years during this period in which US growth was weakest, and on the right are the 15 years in which it was strongest.
What stands out is that in more than half of the worst years, returns from the stock market were still positive. In six of them, the S&P 500 was up more than 20%, even though GDP growth was zero, or negative.
Not quite as striking, but nevertheless noteworthy, is that even in some of the best years for the US economy, the stock market fell. Incredibly, in 1941, when GDP growth was 17.7%, the S&P 500 declined 12.8%.
Understanding the gap
It is clear from these studies that the state of a country’s economy should not be seen as a guide for how its stock market is likely to perform. As MSCI notes, there are three main reasons for this.
“First, in today’s integrated world we need to look at global rather than local markets. Second, a significant part of economic growth comes from new enterprises and not the high growth of existing ones; this leads to a dilution of GDP growth before it reaches shareholders. Lastly, expected economic growth may be built into the prices and thus reduce future realized returns.”
Investors should therefore be cautious about basing their decisions on economic data. This has even been apparent in the UK over the past five years.
The story in London
Since 2014, the local economy has mostly staggered along at growth rates below 2%. Yet, the FTSE All Share Index has delivered an annualised return of 9.4%, which in today’s low inflation environment is a real return of close to 8%.
If an investor had stayed out of the market due to fears around Brexit and the country’s general lack of economic momentum, they would have missed out on this period of growth.
Similarly, those who argue that the US stock market is going to continue to show good returns almost always base their argument at least in part on the fact that the US economy is still strong. As history has shown in the case of Japan, however, a growing economy does not necessarily equate to good returns for investors on the stock market, particularly if share prices are already high.
Trying to guess which markets may or may not deliver the best returns in future based on the economic prospects of the country in which they are based is therefore not a way to investing success. Investors are far better off building a strategy diversified across markets that they can stick to no matter the economic environment, and reap the rewards over the long term.
One of South Africa’s most respected financial journalists, PATRICK CAIRNS is a trusted commentator on the world of investments and the quirks of behavioural finance. Over more than a decade he has built a reputation for keeping the industry honest, and putting the interests of investors first.
If you are interested in reading more of his work, here are his most recent articles for TEBI:
A lesson still worth learning three centuries later
So you think you can pick winning stocks?
What is the value that fund managers are selling?
© The Evidence-Based Investor MMXX