We’ve written many times about the SPIVA scorecard from S&P Dow Jones Indices. But Morningstar has its own ongoing measure of active fund performance, called the Active/Passive Barometer.
The latest instalment of the Barometer has just been published and, as you would expect, the findings are generally in line with SPIVA’s. Broadly speaking, your chances of identifying a fund that will both survive and outperform over the long term are slim. And the notion that active funds fare better than index funds in falling markets is not borne out by the data.
But, as Morningstar’s BEN JOHNSON explains, you can greatly increase the prospects of a successful outcome by choosing a fund with lower fees and charges.
The coronavirus sell-off and subsequent rebound tested the narrative that active funds can navigate market volatility better than their index peers. The mid-year instalment of the Morningstar Active/Passive Barometer looks at active funds’ performance through the first half of 2020 and shows that there’s little merit to this notion. Morningstar Direct clients can download the full report.
Across the 20 Morningstar Categories examined in this latest report, 51% of active funds both survived and outperformed their average index peer during the first half of the year. Active funds’ performance was neither categorically better nor worse than that of their index peers during this period.
When viewed as a whole, active funds had a roughly 50/50 chance of succeeding during the year’s first half, although results varied widely across asset classes and categories. For example, actively managed U.S. stock funds didn’t fare as well as foreign-stock funds. Just 48% of the former cohort outperformed their average passive peer in the first six months of 2020, while nearly 60% of the latter group did.
What about bond funds?
Overall, active bond funds’ showing was relatively poor. From January through June, 40% of active funds in the intermediate core bond, corporate-bond, and high-yield bond categories both lived and beat their average passive counterpart. Many bond funds were caught offside in a period that punished credit risk and rewarded interest-rate risk as credit spreads widened and rates fell.
Longer time horizons are more meaningful
But six months isn’t a sufficient time horizon for investors to draw conclusions regarding their odds of partnering with successful active managers, as their success rates are very noisy over short time frames. They can fluctuate wildly from year to year, depending on what’s going on in the markets and how that reflects on the systematic biases in their portfolios as well as in the indexes we measure them against. For example, many active bond funds tend to take more credit risk than their indexed peers. Their success rates tend to rise when this risk is rewarded and fall when credit markets are roiled, as they were earlier this year.
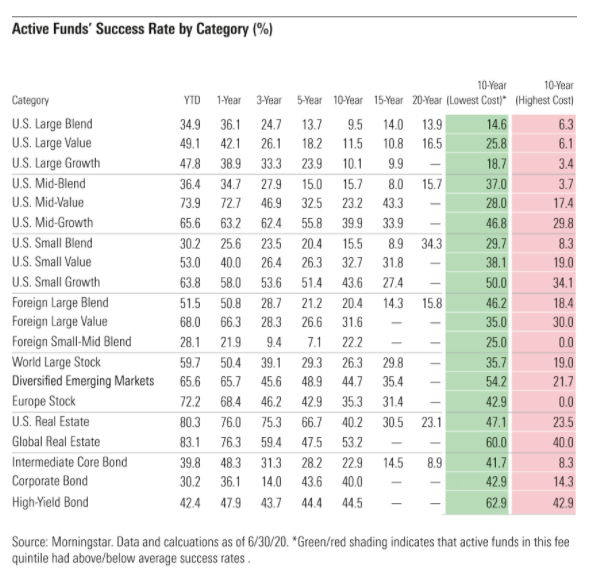
Looking back over longer horizons yields useful signals — data that investors can put into practice while selecting active funds. In general, actively managed funds have failed to survive and beat their benchmarks, especially over longer time horizons. Only 24% of all active funds topped the average of their passive rivals over the ten-year period ended June 2020.
However, success rates vary across categories. Long-term success rates were generally higher among foreign-stock, real estate, and bond funds and lowest among U.S. large-cap funds. Investors can use this data to home in on areas of the market where they have better odds of picking winning funds.
Sizing the payoffs and penalties
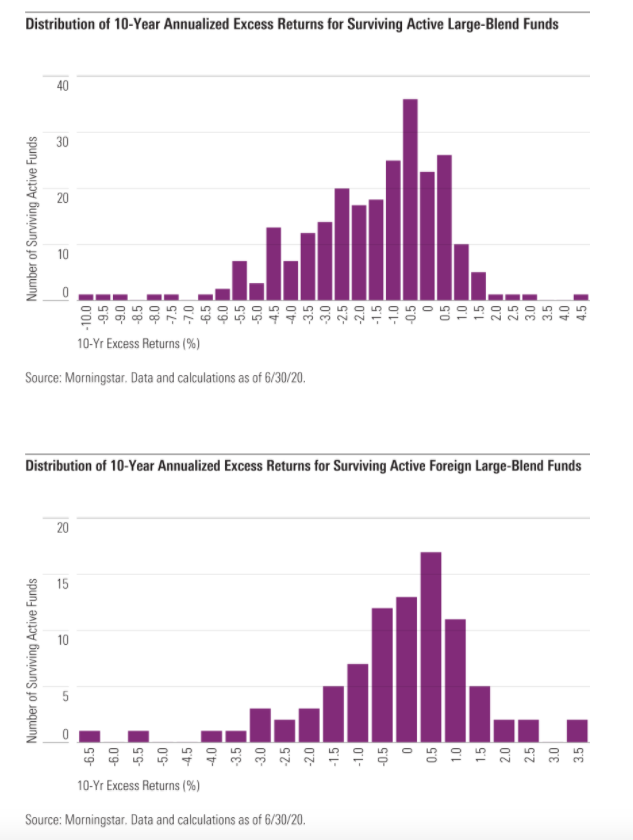
Investors should understand the chances of finding a successful active fund as well as the size of the prospective payout for picking a winner and the penalty for landing on a loser. The Active/Passive Barometer contains this information in the form of plots of the distribution of 1ten-year excess returns for surviving active funds versus the average of their passive peers.
Much like success rates, these distributions vary widely across categories. In the case of U.S. large-cap funds, the distributions skew negative. When considered in conjunction with the low long-term success rates in these categories, this is an indication that the likelihood and performance penalty for picking an underperforming manager tends to be greater than the probability and reward for finding a winner.
The inverse tends to be true of the fixed-income and foreign-stock categories examined, where long-term success rates have generally been higher and excess returns among surviving active managers skewed positive over the past decade. Exhibits 2 and 3 show the distributions of excess returns for surviving active funds from the large-blend and foreign large-blend categories.
Most investors choose above-average funds
All averages have their flaws. And it is a flawed assumption that investors pick average funds.
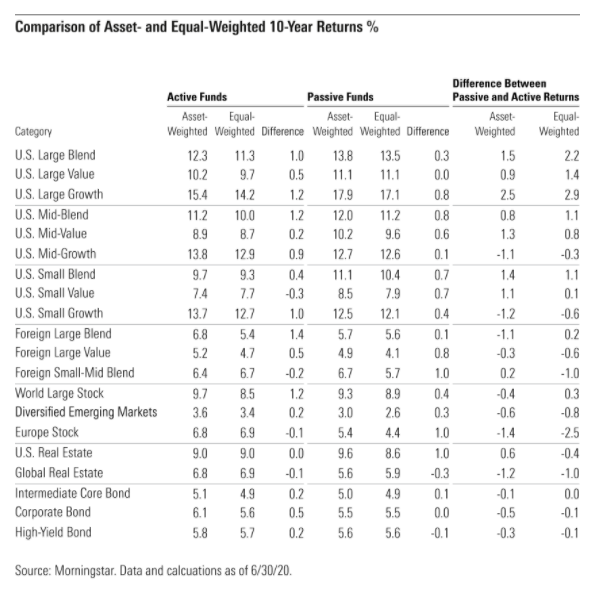
Indeed, the data shows that the average dollar invested in active funds (asset-weighted average return) outperformed the average active fund (equal-weighted average return) in all but four categories over the past 10 years. This implies that investors have favoured cheaper, higher-quality funds.
However, the average dollar in active funds does not always do better than the average dollar invested in passive ones. Looking at the difference between asset-weighted returns for active and passive funds can give investors a sense of where they’ve been best served by active managers.
The second column from the right in Exhibit 4 shows these figures for the 10-year period through June 2020. In general, investors fared better with index funds than active ones in U.S. stock categories and with active funds in fixed-income and foreign stock categories.
Costs matter
The signal that rings loud and clear in this data set is that costs matter. The cheapest funds succeeded about twice as often as the priciest ones (34% success rate versus 16% success rate) over the 10-year period ended June 30, 2020. This not only reflects cost advantages but also differences in survival, as 65% of the cheapest funds survived, whereas 49% of the most expensive did so.
If there’s one near-certainty in investing, it is “you get what you don’t pay for”, as the Vanguard’s late founder Jack Bogle said.
This article was first published in Morningstar Direct’s Research Portal.
For more insights from our friends at Morningstar, take a look at these other recent articles:
Three truths about ESG investing
Fees crucial to ESG investing success — Morningstar
US fund fees cut in half in 20 years
Three risks you take when choosing a thematic fund
Is market-cap indexing a form of momentum investing?
A critical look at the arguments against index investing
US value and growth performance under the microscope
Here are some other recent TEBI posts we think you’ll be interested in:
A strategic approach to rebalancing
What do investors and trial juries have in common?
Why have stocks lagged bonds since 1970?
The cost of anticipating corrections
Is your value fund bad for the planet?
Don’t invest like you were Don Quixote
FIND AN ADVISER
Are you looking for an evidence-based financial adviser? We can help you find one. Click here for more details.
Picture: Sharon McCutcheon via Unsplash
© The Evidence-Based Investor MMXX